~Technology Security Challenges~
We can help you detect a security breach at the device level
With the increase in industrial automation hackers are using this as an opportunity for attacks. An attack may result in severe financial damages, loss of reputation, and breach of confidential information, just to name a few. What are the attack vectors in the IIoT market?
- The IIoT device is used as a window into the industrial enterprise network and database enabling a hacker to corrupt and seize control of the heart of the corporation.
- The hacker attacks the IIoT device causing it to malfunction or stop functioning altogether.
- Control of the IIoT device is seized and turned into a BOT to mount Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks against other industrial enterprises.
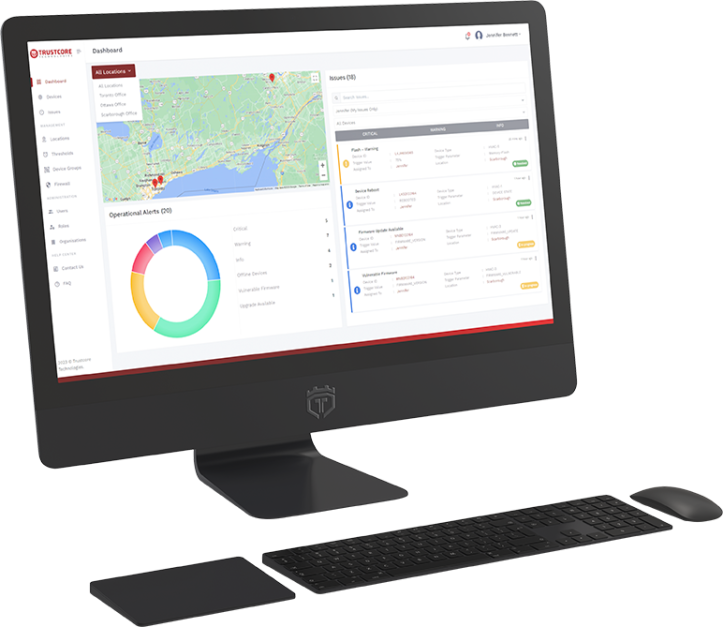

TRUSTCORE BA
Real time behavior analytics and anomaly detection at the Edge
Containerized application, easy install, no additional hardware required
On or Off Premise
Granular visibility
Root cause analysis
Faster Response time
Predictive and Advanced Failure Detection
Smart Buildings
Cyber attackers can gain access to smart buildings through IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) devices. Smart buildings use a range of connected devices, sensors, and systems to monitor and manage various aspects of building operations, such as heating, ventilation, lighting, and security. While these devices can provide significant benefits, they can also introduce vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. One common way attackers can gain access to smart buildings is through exploiting unsecured or poorly secured IIoT devices connected to the building's network. For example, attackers may attempt to gain access to the building's HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) system through an insecure thermostat or other connected device. Once inside the network, attackers can move laterally to other systems and devices, potentially gaining control over building operations or accessing sensitive data. To prevent these types of attacks, it's essential to ensure that IIoT devices connected to a smart building's network are properly secured and regularly updated with the latest security patches.
Factory Automation
Cyber attackers can access factory OT (Operational Technology) networks through IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) devices. IIoT devices are designed to connect various machines and devices within a factory or industrial environment to gather data and enable remote monitoring and control. However, these devices can also introduce vulnerabilities that can be exploited by cyber attackers to gain unauthorized access to factory networks. One common way cyber attackers can exploit IIoT devices is through a technique called "credential stuffing," where they use a list of known usernames and passwords to attempt to gain access to an IIoT device. If the device is using a default or weak password, the attacker can gain access and use it as a foothold to pivot to other devices on the factory network. Another way attackers can gain access is through exploiting unpatched vulnerabilities in IIoT devices. Many IIoT devices run on outdated or unpatched software, which can leave them open to known exploits that attackers can use to gain access. To prevent these types of attacks, it's essential to ensure that IIoT devices are properly secured and regularly updated with the latest security patches.
Water & Utilities
Water treatment plants and utilities are critical infrastructures that ensure the provision of safe drinking water and sanitation services. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) devices play a critical role in monitoring and controlling various processes. However, these devices are increasingly becoming cyber targets due to their connectivity and integration into larger networks. Key devices include SCADA systems, which oversee water treatment operations, and PLCs, which automate machinery control. Smart sensors and meters monitor water quality and other parameters. Valves and actuators regulate flow and chemicals, and HMIs provide interfaces for operators to manage systems. Telemetry systems transmit data from remote sensors, and industrial routers and gateways connect IIoT devices to networks. Wireless sensor networks monitor environmental conditions, and asset management systems track equipment condition for maintenance. Given their critical roles, these IIoT devices are attractive targets for cyber attackers aiming to disrupt operations, steal sensitive data, or cause physical damage.




